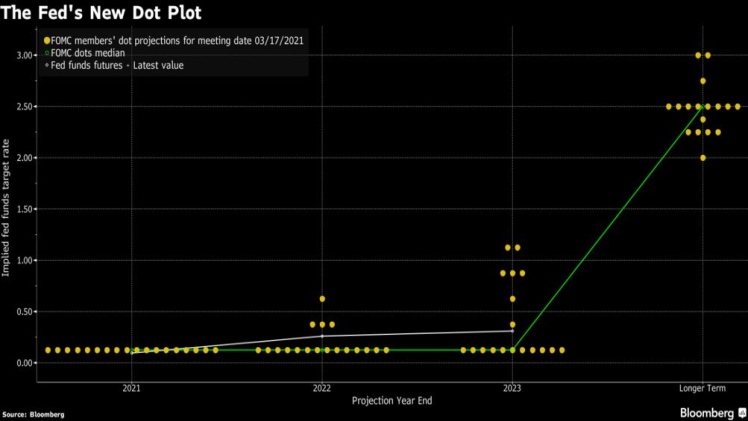
The Federal Open Market Committee meets eight times a year to determine whether to change the United States monetary policy and evaluate the economic and financial conditions. It reviews the unemployment rate, inflation and the level of employment output. Each meeting includes a press conference and a Summary of Economic Projections. The minutes of the meetings are published three weeks after the date of the policy decision.
Federal Open Market Committee
The Federal Open Market Committee is a committee of the Federal Reserve System, which oversees open market operations across the country. It makes key decisions regarding interest rates and money supply. Its mission is to promote economic growth and minimize inflation. Members of the FOMC are chosen from among the nation’s leading financial institutions.
The FOMC’s mission is to set interest rates and money supply, as well as regulate inflation. These decisions have a significant impact on the markets and economy. The FOMC is a central bank that is responsible for the stability of the U.S. economy. Its announcements are among the most highly anticipated trading events of the year, and their effects are significant.
The FOMC meets regularly to set monetary policy, including the discount rate. This rate is the cost of overnight borrowing. It may raise or lower the discount rate or change the federal funds target rate. These decisions are approved by the Board of Governors. The FOMC can also set the discount rate by purchasing and selling government securities. By doing this, the FOMC helps increase the money supply and decrease interest rates. Ready to know all about the when is next fed meeting before trading.
Interest Rate Targeting
Interest rate targeting refers to the process in which the central bank sets a target interest rate for the country’s economy. This rate is determined by an open market operation, which is a series of purchases and sales of debt instruments. The target rate depends on factors such as the supply and demand for overnight lending. In addition, the target rate may affect the prices of goods and services, employment, and foreign exchange rates.
Since the financial crisis in 2007, the Federal Reserve has changed its approach to monetary policy. In late 2008, it adopted a near-zero target for the federal funds rate. This action was meant to push long-term interest rates downward, support economic activity, and make financial conditions more accommodative. In addition, the Fed has greatly increased its holdings of longer-term securities through open market purchases.
Meetings
The Federal Open Market Committee meets eight times a year. Its members discuss changes in monetary policy and economic conditions. They also consider price stability and employment output. The meetings typically last for two days. The meeting minutes are released three weeks after each policy decision is made. They also include links to policy statements.
During meetings, members discuss the economic outlook, the outlook for local and global financial markets, and the state of the economy. In addition, Reserve Bank presidents and the Board of Governors also share their views on monetary policy. In the end, the designated members vote on monetary policy. The most recent FOMC meeting, held on September 2022, raised the fed funds rate by 0.25% to a target range between 3% and 3.25%.
Fed’s Balance Sheet
The Federal Reserve’s balance sheet is a collection of assets and liabilities. The Fed uses the balance sheet to control inflation and manage long-term interest rates. It is expected to grow to around $7 trillion by mid-2020. It has recently expanded its balance sheet to meet various economic challenges. However, it is not willing to quickly unwind it in order to prevent the economy from overheating.
The Fed first used quantitative easing during the 2008-2009 global financial crisis. Since then, the balance sheet has grown to more than $8.9 trillion, and in May 2022 the Fed announced plans to start trimming its holdings. While these moves can help the economy recover, they may also prematurely send the nation into another recession.
Conclusion
The Fed policymaking committee recently raised the key short-term rate, which affects many consumer and business loans. The rate is now at three to three-and-a-half percent, the highest level since early 2008. Powell also indicated that it would be appropriate to slow rate hikes at some point, though he did not provide a timeline. The announcement sent stocks tumbling.